1. General information
This guide is aimed at experienced administrators and its purpose is to provide you with the basic knowledge you need to ensure optimal operation of BMD NTCS. You will find descriptions of the recommended settings concerning the hardware, the operating system, the SQL Server and BMD NTCS.
2. Priorities and importance
First, here are the individual topics that will be described in more detail later sorted by their priority.
Very important:
- Power options
- SQL maintenance plan
- Antivirus software
Important:
- SQL memory
- CPU
- I/O system
- Network
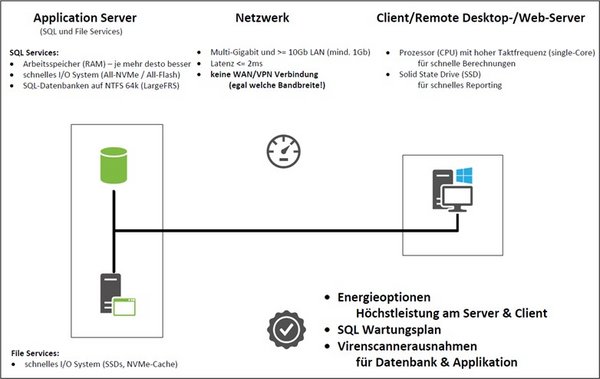
3. Hardware
3.1. Processor (CPU)
Modern processors typically have many cores, allowing them to process multiple processes simultaneously. However, the speed of a system also scales significantly based on the clock speed.
Our recommendation: Use a processor with as high a clock speed as possible.
3.2. Memory (RAM)
There are no special requirements regarding the memory. Depending on size and complexity of the environment, the principle “the more the better” applies—you should also make sure that there are sufficient reserves.
Our recommendation: Be generous and future-oriented when choosing the memory.
3.3. I/O system
Regardless of whether it comes to virtualisation, databases or remote desktop services and virtual desktop infrastructure, a fast I/O system is essential. Please take into account the number of SSDs or HDDs and the selection of the correct RAID type.
Our recommendation: All-Flash – choose NVMe over SATA/SAS.
3.4. Network (Ethernet)
The speed of the network connection depends on both bandwidth and latency. A connection by cable is therefore always faster than a wireless or inter-site connection.
Our recommendation: Use multi-gigabit and ≥ 10GbE connections, latency ≤ 2 ms
Avoid WLAN and do not use WAN/VPN connections.
3.5. BIOS/UEFI and power options
Nowadays, systems are almost always delivered with balanced default power options. Many manufacturers offer various BIOS/UEFI profiles, such as “Static High Performance”, “Performance optimized”, “Maximum Performance”, etc. The purpose of these different profiles is to automatically make the hardware as fast as possible.
Our recommendation: Configure the power options to the highest performance for the hardware.
4. Operating system
4.1. Power options
The default power options for the operating system are usually also balanced. This is the case for Windows and other operating/hypervisor systems.
Our recommendation: Configure the power options to the highest performance on both the server and the client.
More information can, for example, be found under: https://knowledge.broadcom.com/external/article/366987/virtual-machine-application-runs-slower.html
4.2. Antivirus software
Antivirus software is essential and indispensable. It runs silently in the background, but it still affects the performance of the system.
Our recommendation: Make sure to configure appropriate exceptions.
See also:
BMD: Recommended settings for antivirus software
Configure antivirus software to work with SQL Server - SQL Server | Microsoft Learn
5. SQL Server
5.1. Service packs and cumulative updates
Microsoft provides both fixes and enhancements via updates.
Our recommendation: Always keep the SQL Server up to date.
See also:
5.2. Maintenance plan
A maintenance plan is one of the most important things when it comes to the best possible database performance.
Our recommendation: Run the SQL maintenance plan regularly.
See also:
5.3. Memory
The performance of the SQL database depends in large part on the available memory. In order for the operating system to have sufficient resources, you should limit the memory for the SQL instance.
As a rule of thumb, defining 6 GB or 10% of the available memory of the operating system should work (use whichever value is greater).
Example: For 32 GB RAM, you should configure a limit of a maximum of 26,624 MB.
Our recommendation: Adjust the limit for the SQL database based on the available memory.
5.4. File system
For optimum performance, SQL databases (incl. tempdb) should be stored on drives formatted with an NTFS cluster size of 64 KB. For large databases, the large FRS (file record segments) should also be taken into account.
Our recommendation: Format SQL drives with NTFS 64 KB (LargeFRS).
6. BMD NTCS system performance
To get an idea of your system's performance, you can run a performance test in BMD NTCS under ? → Info → System performance. This test determines the respective values for arithmetic operations (CPU performance), file operations (I/O performance) and database accesses.
Our recommendation: Test the performance on both the server and the client.